Malaysia – Let’s explore here

What’s it like in Malaysia?
Malaysia is a stunningly beautiful country in south eastern Asia, that’s split across two different land masses separated by the South China Sea. The peninsular part is located at the bottom tip of Thailand; the other shares the island of Borneo. Both parts are mainly hilly with forested mountains, and coastal plains. The highest point is Mount Kinabalu, on the island of Borneo, at 13,435 ft (4,095 m) above sea level.
It’s about 1½ times the size of the UK, and shares land borders with Thailand, Brunei and Indonesia; it also shares a causeway with Singapore.
The population of Kazakhstan is around 34½ million people (2024), about one in four of whom live in the metropolitan area of the capital, Kuala Lumpur. It relies heavily on its oil reserves.
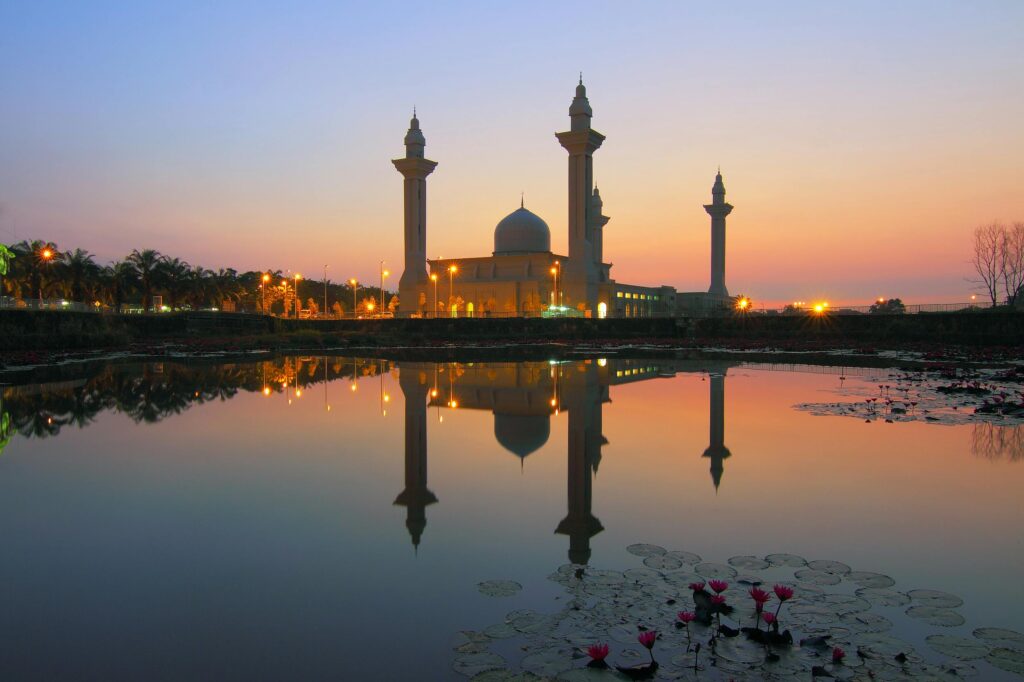

A bit about the history of Malaysia
Early History and Ancient Kingdoms
Malaysia’s history dates back to ancient times, with evidence of early human settlements, particularly in the Malay Peninsula and Borneo. Ancient kingdoms such as the Srivijaya Empire (7th to 13th centuries) and the Majapahit Empire (13th to 16th centuries) were influential in the region. These kingdoms controlled key trade routes and were instrumental in spreading Hinduism, Buddhism and Islam to the region.
Islamic Influence and the Sultanates
By the 15th century, the spread of Islam transformed the Malay Peninsula. The Malacca Sultanate, founded in 1400, became a powerful maritime empire that controlled the Strait of Malacca, one of the most important trade routes in the world. The sultans of Malacca were pivotal in spreading Islam in the region and establishing Malaysia’s Islamic heritage.
Colonial Era
In the 16th century, European powers began to establish control over parts of Malaysia. The Portuguese captured Malacca in 1511, followed by the Dutch in 1641, and eventually, the British took control, establishing protectorates in the Malay states. British rule in Malaya primarily focused on rubber and tin industries, with significant migration of Chinese and Indian workers to support these economic activities. Meanwhile, the British also controlled the island of Borneo, specifically Sarawak and Sabah, which became part of British North Borneo. The British presence in Malaysia led to significant social and economic changes, creating a diverse multi-ethnic society, although it also led to tension and unrest, especially during World War II.
World War II and Japanese Occupation
During World War II, the Japanese invaded Malaya and occupied it from 1942 to 1945. The Japanese occupation was marked by hardship, economic disruption and resistance from local groups. The end of World War II saw the return of British rule, but this period also fostered growing nationalist movements that demanded independence.
Path to Independence
Following World War II, the push for independence grew stronger. The Malayan Union, which was proposed by the British in 1946, faced strong opposition from the local Malay population. This led to the formation of the Federation of Malaya, a political union between the Malay states and the Straits Settlements, which eventually gained full independence from British on August 31, 1957.
Formation of Malaysia
In 1963, the Federation of Malaya, Singapore, and the British colonies of Sarawak and Sabah united to form Malaysia. Singapore was later expelled from Malaysia in 1965 after political disagreements. The formation of Malaysia marked the unification of the various territories on the Malay Peninsula and Borneo under one national government.
Post-Independence and Economic Growth
In the years following independence, Malaysia experienced significant economic development, particularly after the 1970s. The country shifted from an economy based on agriculture and mining to one that was more industrialised, focusing on electronics, manufacturing and services. This economic boom helped reduce poverty and improve living standards for many Malaysians.
Political and Social Development
Malaysia’s political landscape has been dominated by the United Malays National Organisation (UMNO), which has led the government for much of its post-independence history. UMNO has been a key player in the Barisan Nasional coalition, which has governed Malaysia for decades. Malaysia’s political system is based on a constitutional monarchy, with the King serving as a ceremonial head of state. Over the years, Malaysia has faced political challenges, including issues related to corruption, ethnic and religious tensions, and political dissent. In 2018, the opposition coalition Pakatan Harapan won a historic election, ending UMNO’s long reign and leading to the appointment of the country’s first non-UMNO prime minister.
Modern Era and Challenges
In the 21st century, Malaysia has continued to be one of south east Asia’s most dynamic economies, with a growing middle class, a strong manufacturing sector and a robust tourism industry. However, the country faces challenges such as political instability, inequality and environmental issues, including deforestation and urbanisation. Malaysia remains a multicultural society, with Malays, Chinese and Indians forming the three main ethnic groups. The government has worked to maintain national unity through policies that promote economic development, while also addressing ethnic and religious diversity.
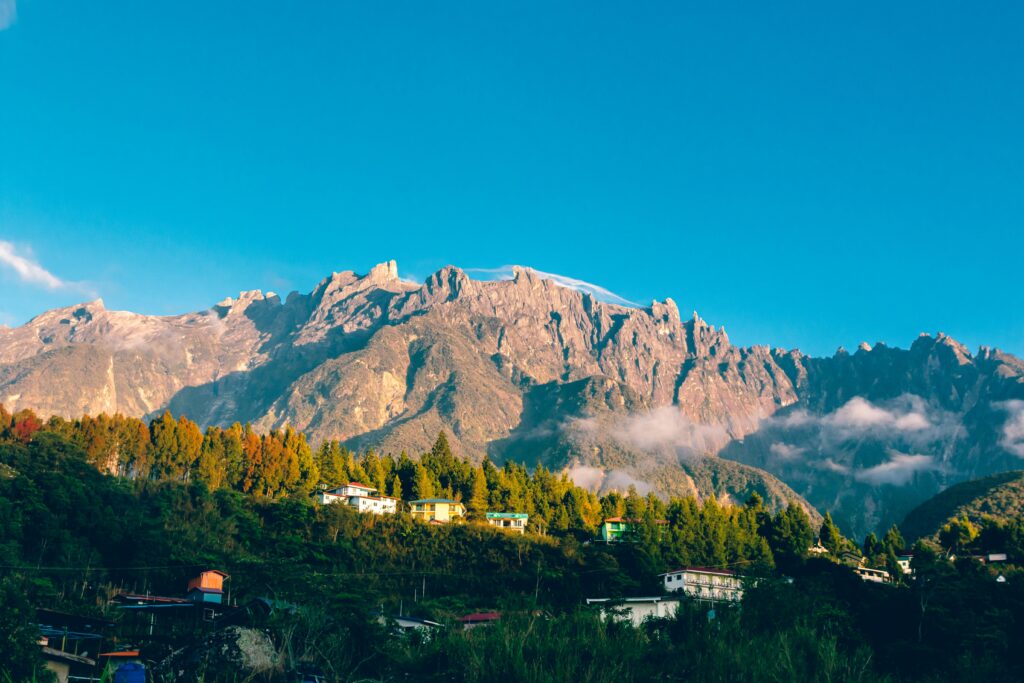

Malaysia road trip
We haven’t finished our planning for our road trip trhough Malaysia yet. When we do though, we’ll post it here, and in the blog.
Hopefully our journey will improve our knowledge of this intriguing and beautiful country, and enable us to meet some interesting people. We’ll be updating this page at that time – don’t forget to check back 🙂
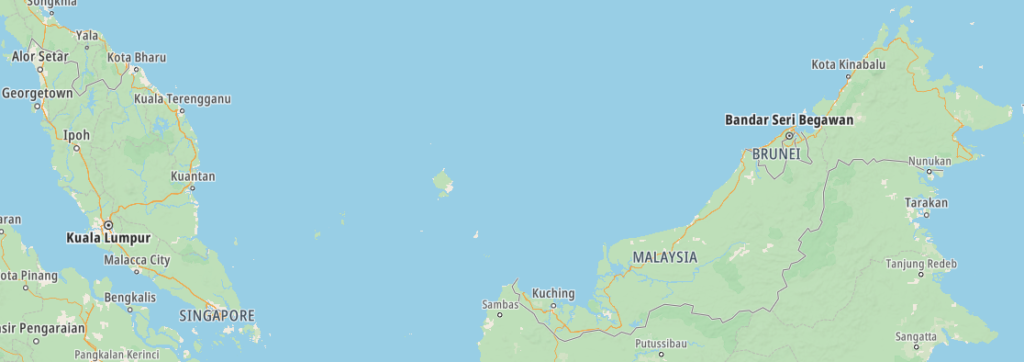
Map of Malaysia
What’s it like to drive in Malaysia?
They drive on the left hand side of the road in Malaysia. In the main, roads are quite good. Driving standards are also quite good.
Do you require an international driving permit in Malaysia?
We’ve created a dedicated page to driving abroad, which answers this question, and more, which you might find helpful.
Can you use your UK driving license when driving through Malaysia?
We’ve created a dedicated page to driving abroad, which answers this question, and more, which you might find helpful.
Do I need a carnet de passages to drive in Malaysia?
A carnet de passages is required to overland in Malaysia. We’ve created a dedicated page to driving abroad, which answers this question, and more, which you might find helpful.
What currency do they use in Malaysia?
In Malaysia they use the Malaysian ringgit. Cash is widely used. The use of credit / debit cards is widely accepted. Travellers cheques are not readily accepted outside of major city banks. There are many ATMs in cities and towns throughout the country.
You should make yourself aware of the amount that your bank charges you for using credit and debit cards abroad. Often credit cards are cheaper for purchasing items directly, and for withdrawing cash from ATMs.
What language do they speak in Malaysia?
They speak Malay in Malaysia. English is also widely spoken, as is Mandarin.
What time zone is Malaysia in?
Remember, when you’re planning your next trip to take a look at what time zone it’s in.
Do I need a visa to visit Malaysia?
We’ve created a dedicated, more comprehensive page on visas, which you should find helpful. Check it out!
Is wild camping legal in Malaysia?
Yes, wild camping is fine in Malaysia.
What plug / socket type do they use in Malaysia?

In Malaysia they use plug / socket type G.
Health issues in Malaysia
Is it safe to drink water in Malaysia?
Yes, it is safe to drink tap water in Malaysia. Bottled water is also readily available across the country.
What vaccinations are required for Malaysia?
This NHS website is kept up to date with all relevant information on vaccinations in Malaysia.
Phones in Malaysia
What is the country calling code for Malaysia?
The country calling code for Malaysia is +60
What are the emergency phone numbers in Malaysia?
- The emergency number for police in Malaysia is: 112 / 999
- In Malaysia, the emergency number for ambulance is: 112 / 999
- The emergency number for fire in Malaysia is: 112 / 999
If you’ve got some useful info that you’d like to share, let us know!
And don’t forget to check out all the other pictures!
