Mainland Netherlands – Let’s explore here
What’s it like in the Netherlands?
Mainland Netherlands is part of the Kingdom of the Netherlands. The mainland is located in western Europe, although the Kingdom also consists of some islands in the Caribbean, namely Aruba, Bonaire, Curaçao, Saba, Sint Eustatius and Sint Maarten.
Its population is around 18 million people (2025), about 2½ million of whom live in the metropolitan area of the capital, Amsterdam, making it one of the most densely populated countries in the world. It is the land of multi-linguists, very tall people, and super friendly, liberal and very direct people!
In Europe it has land borders with Belgium and Germany, and is a very flat country – more than a quarter of it lies below sea level! The highest point is Vaalserberg hill at 1,059 ft (323 m) above sea level.
Despite being so small, and despite having to reclaim the sea just to have enough land for the ever increasing population, it’s had such a big impact on the world.
By the way, the Netherlands officially dropped its support of the word Holland for the whole country in January 2022.

A bit about the history of the Netherlands
Early History and Formation
The area now known as the Netherlands has been inhabited since prehistoric times. By the Roman period, the region was part of the Roman Empire, and it was later controlled by various Germanic tribes after the fall of Rome. In the Middle Ages, the region was divided into several small feudal territories, including parts of the Holy Roman Empire.
The Dutch Revolt and the Formation of the Dutch Republic
In the late 16th century, the region, then part of the Habsburg Empire, began to resist Spanish rule. The Dutch Revolt (1568-1648) was a struggle against Spanish dominance and led to the formation of the Dutch Republic in 1581. The peace treaty that ended the revolt, the Treaty of Westphalia in 1648, recognised the independence of the Dutch Republic, which was also known as the United Provinces of the Netherlands.
Golden Age
The 17th century was a period of remarkable growth and prosperity for the Netherlands, known as the Dutch Golden Age. The country became a global maritime power, establishing a vast colonial empire in Asia, Africa, and the Americas. Amsterdam became a leading center of trade, finance and art, and Dutch painters such as Rembrandt and Vermeer flourished during this time.
Decline and Struggles in the 18th Century
In the 18th century, the Dutch Republic began to decline due to economic difficulties, military conflicts, and political instability. The country was drawn into wars with France and Britain, and its once-dominant role in global trade was challenged by rising powers like Britain. In 1795, the Batavian Republic was established, which was essentially a French client state under Napoleon Bonaparte.
Napoleonic Period and the Kingdom of the Netherlands
After Napoleon’s defeat in 1815, the Congress of Vienna created the Kingdom of the Netherlands, combining the Netherlands, Belgium and Luxembourg under one monarch. However, the union was short-lived, as Belgium rebelled in 1830 and became an independent state. The Netherlands retained control of Luxembourg, though it also became a constitutional monarchy.
Industrialisation and Modernisation
In the 19th century, the Netherlands underwent industrialisation, leading to economic growth and urbanisation. The country maintained a neutral position during World War I, although it faced economic hardship due to the war. In the interwar period, the Netherlands was a parliamentary democracy and worked to modernise its economy and infrastructure.
World War II and Aftermath
During World War II, the Netherlands was invaded by Nazi Germany in 1940. The Dutch royal family went into exile in Britain, and the country suffered greatly under occupation. The war ended in 1945 with the liberation of the Netherlands by Allied forces. After the war, the country experienced significant reconstruction and became a founding member of major international organisations, including the United Nations, NATO, and the European Economic Community (EEC), which later became the European Union.
Post-War Period and Modern Netherlands
In the post-war period, the Netherlands experienced rapid economic growth, known as the ‘Dutch Miracle’, and developed a welfare state. The country became one of the most prosperous and socially progressive nations in Europe, with a strong emphasis on human rights, environmental protection, and international diplomacy.
Today, the Netherlands is a constitutional monarchy with a parliamentary system. It is known for its high standard of living, vibrant culture, and active role in international politics. The country remains a member of the European Union, NATO, and many other international organizations.

Netherlands road trip
Map of our road trip through the Netherlands
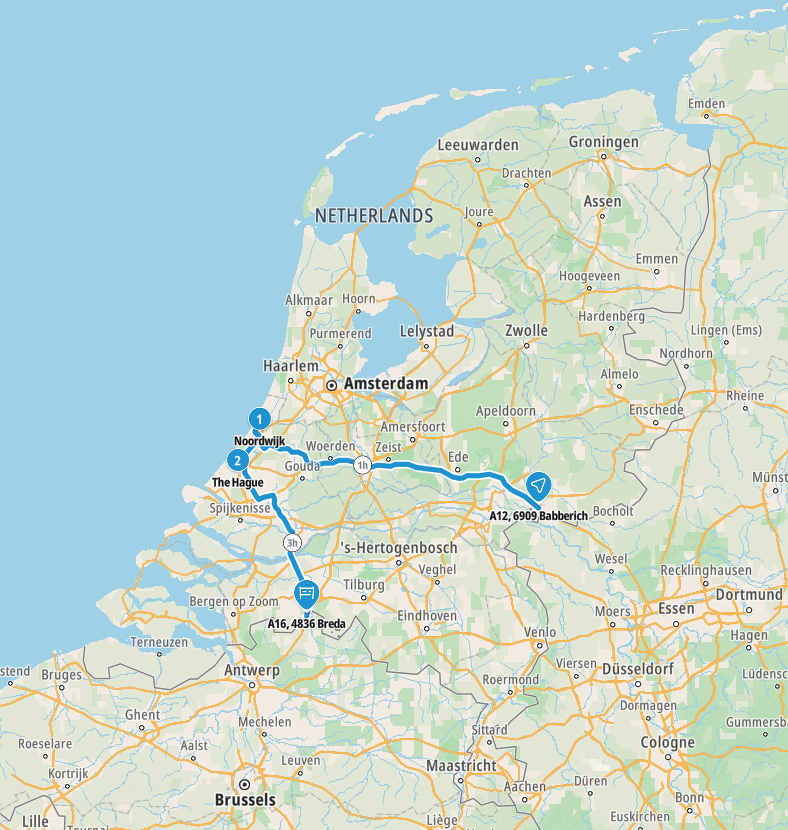
Past road trips in the Netherlands
We created a blog for our 2023 road trip to the Netherlands. You may find it helpful, and you may pick up some tips, or more likely mistakes not to make that we’ve made 😉 Our Netherlands road trip was part of a much larger European road trip.
On our 2023 road trip we travelled from Luxembourg, via Belgium up through the east of the country to Laren near the Sagenlandroute (see below), before heading onto Germany. We avoided all toll roads and motorways on the way, which meant that the route was quite long, but eventful and pretty.
We stayed in an amazing B&B on the 500km Pieterpad hiking route – if you’re in the area, we highly rate it. The owners are incredibly friendly and really helpful. the accommodation is superb, and the scenery is excellent. They even bake bread for your breakfast!



Our favourite places in the Netherlands
These are some of the best places that we explored on our road trips through the Netherlands. We’ve put them in alphabetical order.
We lived in the Netherlands for a short time and have visited many times since. Some of our favourite places include Amsterdam, Arnhem, Appeldoorn, Den Haag, Eindhoven, Epe, Groningen, Noordwijk, Rotterdam … too many to mention!
Den Haag – The Hague
Den Haag is a lovely, large city on the west coast of the Netherlands, and home to the country’s government and royal family. There are around 880,000 people living in the immediate area (2021)
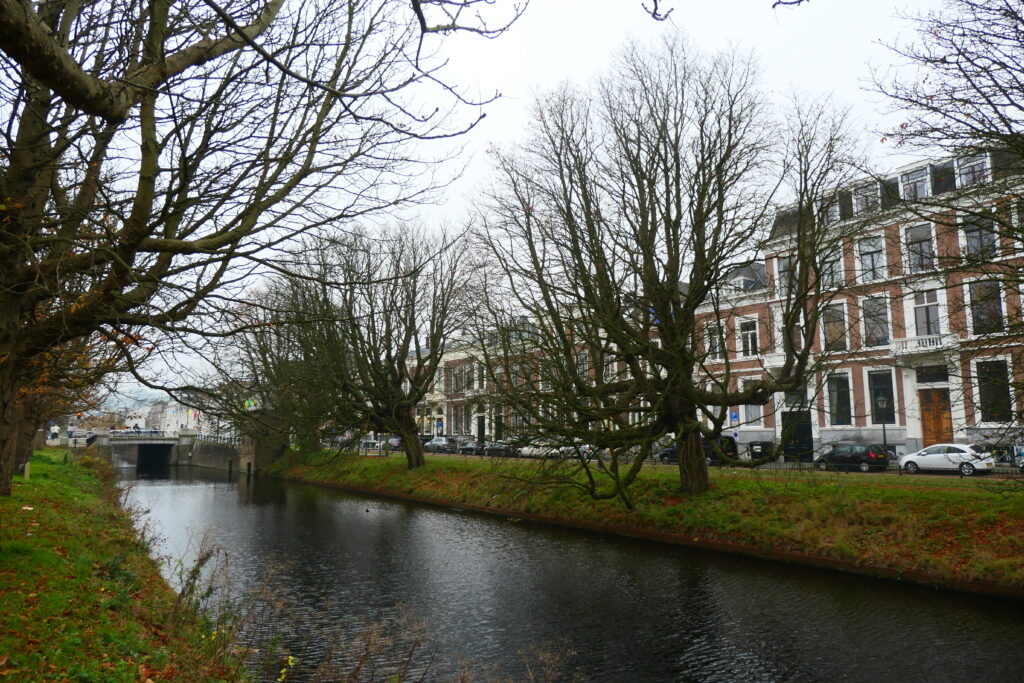



Noordwijk
Noordwijk is a small, very pretty town on the west coast of the Netherlands that has a lovely beach. It’s also the location of Space Expo, the museum and visitors centre for the European Space Agency.


Sagenlandroute – Route of the land of legends
These maps show the route taken when travelling on the Sagenlandroute and its general location within the country. This route is officially endorsed within the country.
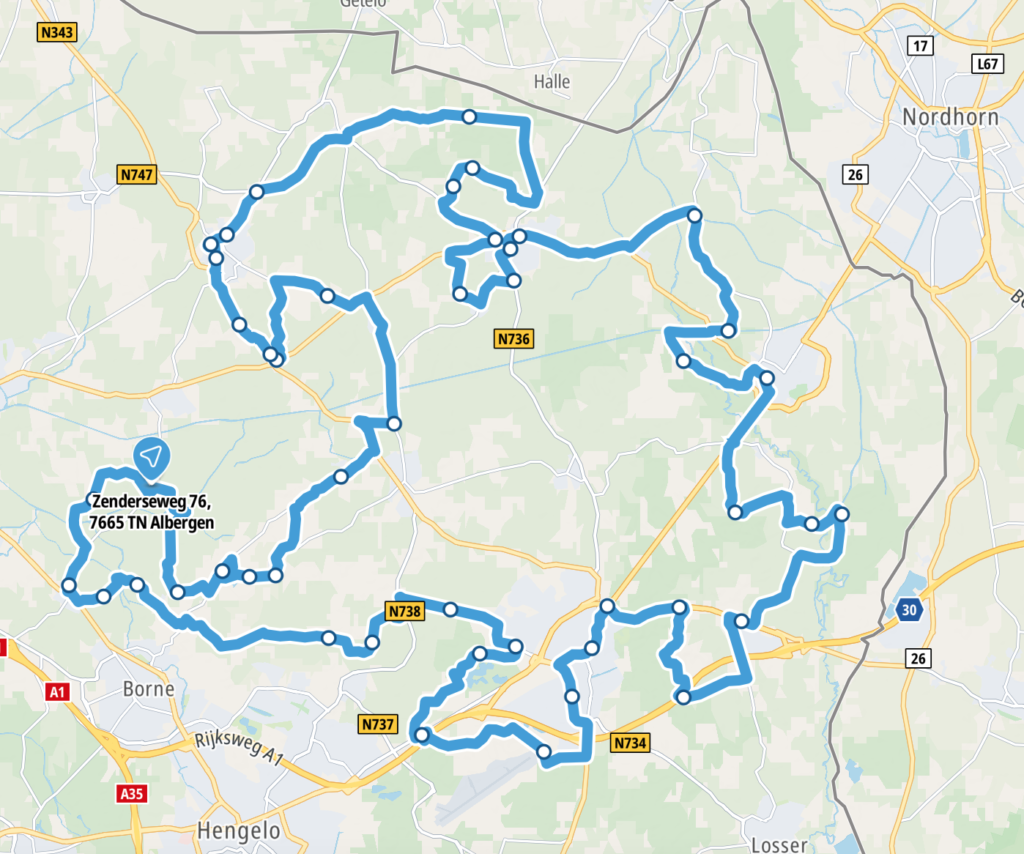
What’s it like to drive in the Netherlands?
As with almost everywhere on the continent of Europe, they drive on the right hand side of the road in the Netherlands.
Traffic police in the Netherlands
Driving in the Netherlands for the most part is very similar to driving in the UK. There are a lot of traffic police, so people tend to drive quite slowly and courteously in the main. Watch out for the traffic police if you’re travelling from Germany into the Netherlands, as the traffic police are always at the border roads ensuring that you don’t continue driving without a speed limit, as in Germany.
Cycling in the Netherlands
The country has vastly expanded its cycling routes. Bicycles are king in the Netherlands – people of all ages ride them everywhere. In fact, more than a quarter of all journeys are made by cycling. Many roads now have as much as a third of each side of the road dedicated to the bike, leaving on third in the central area to drive on. Clearly, with oncoming traffic, you move to the side and sit behind cyclists. However in the countryside, we found that quite often older cyclists do not move from the centre of the road, as clearly they feel that they have right of way, and the car is an annoyance! 😉
Single track roads
Also, many roads in the east of the country are very narrow, and thus you share the road with oncoming traffic. This is fine until you find yourself up against a massive lorry coming the other way, and there are dykes on either side of the road!!
Driving in Amsterdam
Driving in Amsterdam, as with all major cities can be a pain. It’s good to be aware of traffic from all directions, as trams also operate and cycling is very popular. Also, due to the popularity of Amsterdam’s liberal attitude towards recreational drug use, there are lots of tourists that may not be fully aware of where they are going! 😉
Hitchhiking areas in the Netherlands
At the exit from some towns there are designated areas for hitchhiking, which can be helpful should you wish to travel for free.
Do you require an international driving permit in the Netherlands?
We’ve created a dedicated page to driving abroad, which answers this question, and more, which you might find helpful.
Can you use your UK driving license when driving through the Netherlands?
We’ve created a dedicated page to driving abroad, which answers this question, and more, which you might find helpful.
Do I need a carnet de passages to drive in the Netherlands?
We’ve created a dedicated page to driving abroad, which answers this question, and more, which you might find helpful.
What are the speed limits in the Netherlands?
The speed limits for cars in the Netherlands are:
- 80 mph (130 km/h) on motorways
- 30 mph (50 km/h) for urban driving
- 50 mph (80 km/h) outside of built up areas
- 60 mph (100 km/h) on dual carriageways
What currency do they use in the Netherlands?
In the Netherlands they use the Euro. The use of credit / debit cards is now widespread. Travellers cheques are accepted. There are lots of ATMs.
You should make yourself aware of the amount that your bank charges you for using credit and debit cards abroad. Often credit cards are cheaper for purchasing items directly, and for withdrawing cash from ATMs.
What language do they speak in the Netherlands?
They speak Dutch in the Netherlands, although more than 9 in 10 people can also speak fluent English. German, Friesen and French are also spoken.
What time zone is the Netherlands in?
Remember, when you’re planning your next trip to take a look at what time zone it’s in.
Do I need a visa to visit the Netherlands?
We’ve created a dedicated, more comprehensive page on visas, which you should find helpful. Check it out!
Is wild camping legal in the Netherlands?
No, wild camping is illegal in the Netherlands.
What plug / socket type do they use in the Netherlands?
In the Netherlands they use plug / socket types C and F.


Health issues in the Netherlands
Is it safe to drink water in the Netherlands?
Yes, it is safe to drink tap water in the Netherlands. Bottled water is also readily available across the country.
What vaccinations are required for the Netherlands?
This NHS website is kept up to date with all relevant information on vaccinations in the Netherlands.
Phones in the Netherlands
What is the country calling code for the Netherlands?
The country calling code for Albania is +31
What are the emergency phone numbers in the Netherlands?
- The emergency number for police in the Netherlands is: 112
- In the Netherlands, the emergency number for ambulance is: 112
- The emergency number for fire in the Netherlands is: 112
If you’ve got some useful info that you’d like to share, let us know!
And don’t forget to check out all the other pictures!
