Canada – Let’s explore here
What’s it like in Canada?
Canada is the second largest country in the world (after Russia), and has the world’s longest coastline, at 125,000 miles (202,000 km). The border with the USA is the longest in the world, at 5,525 miles (8,891 km) long. Its population however, is only 40 million (2023), making it one of the least densely populated countries in the world. The capital, Ottawa, is home to around one million people. Canada is also home to the world’s northernmost settlement – on the northern tip of Ellesmere Island – 508 miles (817 km) from the North Pole.
What are the main geographical features of Canada?
Much of Canada is forest, with vast ice sheets in the north. The west is dominated by the Rocky Mountains, which stretch 3,000 miles (4,800 km) from the northernmost part of western Canada, to the south western United States. The highest point in Canada is Mount Logan, at 19,551 ft (5,959 m) above sea level. The Appalachian mountains lie in the north east of the country. The Canadian Shield; a large region of exposed Precambrian rock; encircles Hudson Bay, and spans eastern, northeastern, and east-central Canada.
Canada has over two million lakes, including the Great Lakes region, e.g. Lake Superior, Lake Ontario, and Lake Erie. The St. Lawrence River connects the Great Lakes to the Atlantic, and the Mackenzie River and Fraser River are also significant waterways. Canada is also home to Niagara Falls, one of the most famous natural landmarks in the world.

A bit about the history of Canada
Before European arrival, Canada was inhabited by diverse Indigenous peoples, including the First Nations, Inuit, and Métis. The first European exploration occurred in 1497 when John Cabot arrived in Newfoundland, and the French established a permanent settlement in Quebec in 1608 under Samuel de Champlain. The French and British fought for control of North America, culminating in the British taking control of New France after the Seven Years’ War (1763).
Following the American Revolutionary War, British loyalists settled in Canada. The War of 1812 between British and the US helped solidify Canadian identity. In 1867, the British North America Act united Ontario, Quebec, Nova Scotia, and New Brunswick into the Dominion of Canada, marking the beginning of Canadian Confederation. The country expanded westward, with the completion of the Canadian Pacific Railway in 1885. Canada played significant roles in both World Wars and gradually gained independence from Britain through the Statute of Westminster (1931) and the Constitution Act of 1982.
Today, Canada is a bilingual, multicultural country and a constitutional monarchy with a strong economy, a high standard of living, and a reputation for peacekeeping and human rights. The relationship with Indigenous peoples remains an important and evolving issue in the country’s history.



Canada road trip
On our next road trip through Canada, we plan to travel from east to west, starting off in Newfoundland. No doubt the route will vary as we travel through this expansive and beautiful country 🙂
We’d love to travel to some of the more northern states, however we’ll have to plan carefully for this, due to the extreme weather conditions that can quickly develop.
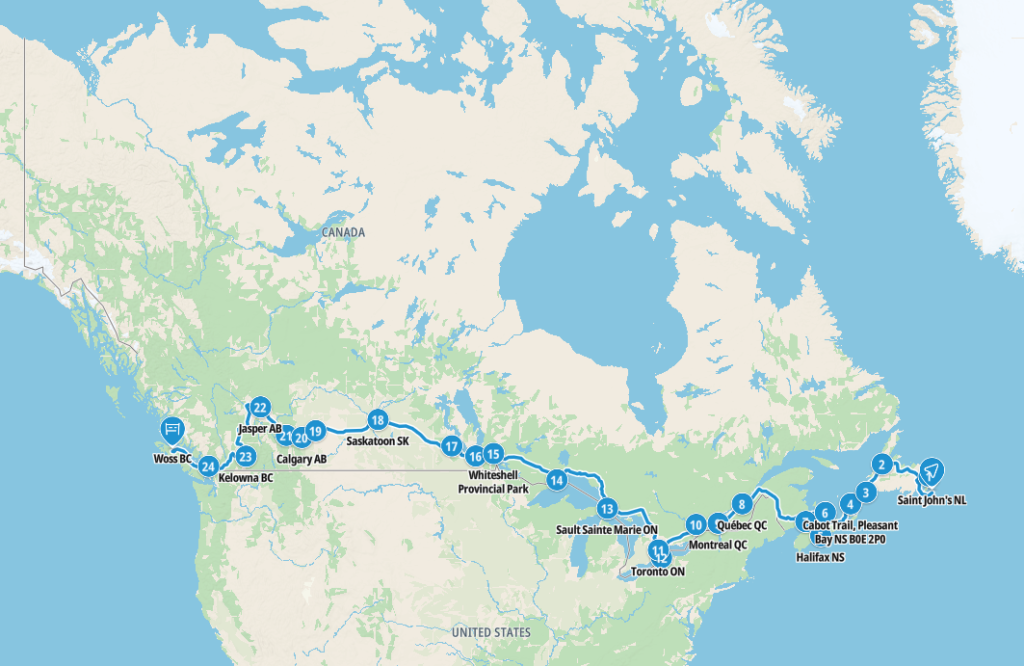
Map of our road trip through Canada
This is a map of our planned road trip that we’ll take on our travels. The route is around 6,000 miles (9,650 km) long.
Our route takes us from St John’s – Elliston – Gros Morne National Park – Port aux Basques – Cabot Trail – Halifax – Charlottetown – Fundy National Park – Québec – Montreal – Ottawa – Toronto – Niagara Falls – Sault Sainte Marie – Thunder Bay – Whiteshell Provincial Park – Winnipeg – Riding Mountain – Saskatoon – Drumheller – Calgary – Banff – Jasper – Kelowna – Vancouver – Vancouver Island
What is the climate like in Canada?
Canada’s climate is highly diverse due to its large size and geographical features, varying from Arctic conditions in the north to temperate climates in the south.
- Northern Canada experiences an Arctic climate, with extremely cold winters and short, cool summers. In some regions, particularly the Northwest Territories and Nunavut, temperatures can drop below -40°C (-40°F) in winter.
- The Prairie provinces (Alberta, Saskatchewan, and Manitoba) are characterized by a continental climate, with hot summers and cold winters. Winters can see temperatures as low as -30°C (-22°F), while summer temperatures can exceed 30°C (86°F).
- The coastal regions, such as British Columbia’s Pacific coast, have a maritime climate, characterized by milder, wetter winters and cooler summers. For example, Vancouver experiences average winter temperatures around 0-5°C (32-41°F).
- Eastern Canada, including Quebec and parts of Ontario, experiences a humid continental climate, with cold winters and warm, humid summers.
- The Atlantic provinces (Newfoundland and Labrador, Nova Scotia, New Brunswick, and Prince Edward Island) typically have a mix of maritime and continental climates, with cold, snowy winters and cool to warm summers.
What’s it like to drive in Canada?
They drive on the right hand side of the road in Canada. Road conditions are generally quite good, as are driving standards.
In winter, roads are often closed because of snowstorms and avalanches in Alberta, British Columbia and other provinces. Check local weather conditions on The Weather Network.
Do you require an international driving permit in Canada?
We’ve created a dedicated page to driving abroad, which answers this question, and more, which you might find helpful.
Can you use your UK driving license when driving through Canada?
We’ve created a dedicated page to driving abroad, which answers this question, and more, which you might find helpful.
Do I need a carnet de passages to drive in Canada?
We’ve created a dedicated page to driving abroad, which answers this question, and more, which you might find helpful.
What are the speed limits?
The speed limits for cars in Canada vary by state, but typically are:
- 30 mph (50 km/h) for urban driving
- 50 mph (80 km/h) outside of built up areas
- 60mph (100 km/h) on dual carriageways
- 60 mph (100 km/h) on motorways
What currency do they use in Canada?
In Canada they use the Canadian dollar. Cash is widely used. The use of credit / debit cards is widely accepted . Traveller’s cheques are accepted in cities and tourist areas. There are ATMs throughout Canada, although not all accept foreign issued cards.
You should make yourself aware of the amount that your bank charges you for using credit and debit cards abroad. Often credit cards are cheaper for purchasing items directly, and for withdrawing cash from ATMs.
What language do they speak in Canada?
They speak English and French in Canada.
What time zone is Canada in?
Remember, when you’re planning your next trip to take a look at what time zone it’s in.
Do I need a visa to visit Canada?
We’ve created a dedicated, more comprehensive page on visas, which you should find helpful. Check it out!
Is wild camping legal in Canada?
Yes, wild camping is fine in Canada.
What plug / socket type do they use in Canada?
In Canada they use plug / socket types A and B.


Health issues in Canada
Is it safe to drink water in Canada?
Yes, it is safe to drink tap water in Canada. Bottled water is also readily available across the country.
What vaccinations are required for Canada?
This NHS website is kept up to date with all relevant information on vaccinations in Canada.
Phones in Canada
What is the country calling code for Canada?
The country calling code for Canada is +1
What are the emergency phone numbers in Canada?
- The emergency number for police in Canada is: 911
- In Canada, the emergency number for ambulance is: 911
- The emergency number for fire in Canada is: 911
If you’ve got some useful info that you’d like to share, let us know!
And don’t forget to check out all the other pictures!
